Presentation [PDF]
Tag Archives: PDF
Dinei Florncio
Cormac Herley
Presentation [PDF]
Twitter transcript
#weis2011 New threat model (that may scale). Rather than use individual users & attackers, use population of users, pop of attackers
#weis2011 assumption/proposition: attacker attacks when Expected{gain} > Expected{loss}
#weis2011 (me) more good math on the slides. using the populations, they made a probability model to predict detection/succumb/gain & cost
#weis2011 model has a core of "sum of efforts defense" (vs weakest link)
#weis2011 attacks are proven unprofitable if prob of success is too low or gain is too low < this may seem obv. but it's an intersting model #weis2011 (me) really good examples of practical example of model efficacy. mimics/validates 2011 DBIR results (does not mention DBIR) #weis2011 working though another example of using "dog's name" as password. (me) this could be a *rly* handy tool for threat modeling #weis2011 Security does not mean avoiding harm, and avoiding harm is less expensive than being secure. #weis2011 "Thinking like an attacker" does not end when an attack is found. Ask how you can use what you found to your advantage.
By now, many non-IT and non-Security folk have heard of Firesheep, a tool written by @codebutler which allows anyone using Firefox on unprotected networks to capture and hjijack active sessions to popular social media sites (and other web sites). The sidebar/extension puts an attactive and easy-to-understand GUI over a process that “real” security people have been using for as long as there has been http-based sessions.
I’ve been using Firesheep quite a bit in non-echo-chamber demos to help illustrate some of the core issues facing enterprises and individual users. A big question that comes out of each demo is “what can I do to safeguard my access to Facebook?”. I provide quick guidance on-the-spot to interested individuals and wanted to share what I communicate to them here both to help a broader audience and get feedback on other steps users can take to safeguard their connections.
General Guidance
The first action I tell users to take is an anti-action: if at all possible, never use free/unsecured Wi-Fi connections. While there are ways of grabbing sessions and other data on wired or secure Wi-Fi networks, the means to do so are beyond the capabilities of most Firesheep users. The danger is still present and you should always consider how much you trust the network you are on when accessing anything on the Internet, but the risk is greatly diminished.
If users are unable or unwilling to follow that first action (and even if they do avoid insecure networks) I then instruct them to ensure that all services they access always use “https“ (SSL/TLS) which encrypts the communication and prevents tools like Firesheep from working. It still – much like the first action – doesn’t stop determined & skilled attackers.
I then caution users on smartphones and tablets to also make sure any applications they use also communicate over SSL. This is far too easy to overlook and can leak data just as easily as a web browser. Tablet & smartphone users can also switch to only using 3G connections to make it that much more difficut for otherrs to eavesdrop.
Finally, I suggest using a virtual private networking (VPN) service such as PureVPN to secure all their connections – not just browser sessions – on public networks (secured or otherwise). SSL/TLS connections are potentially susceptible to what is called a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack [SANS Reading Room (PDF)] and one way to mitigate that threat is to use a VPN to secure all network communication using a more robust/holistic solution. PureVPN (and other, similar good services) are not free, but $5.00-10.00USD per month is not much to pay for personal data security on-the-go.
The Elephant In The Room
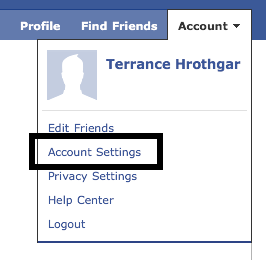
![]() For some reason, even with that general guidance, the whole concept of someone hijacking their Facebook account really scares folks and many end up asking specific question on ensuring their Facebook access is protected. This usually involves walking them through how to check to see if SSL is enabled by Facebook’s service and also how to monitor access to their Facebook account.
For some reason, even with that general guidance, the whole concept of someone hijacking their Facebook account really scares folks and many end up asking specific question on ensuring their Facebook access is protected. This usually involves walking them through how to check to see if SSL is enabled by Facebook’s service and also how to monitor access to their Facebook account.
Unsurprisingly, Facebook does not make setting SSL as a default an easy task. It’s unintuitively not under any “privacy” settings. Instead, you need to navigate down to account settings and poke around to get to the right areas. The screen captures below show the navigation sequence. You’ll notice that this account does not have security enabled since it’s the one I use for demos (I do not have a personal Facebook account).
You’ll also notice that you can have Facebook send you an e-mail when there is an access to your account from an unknown device and also review recent activity on your account. This gives you the ability to be in control as much or as little as you desire.
Homeward Bound
I usually close with guidance on securing your home Wi-Fi network. Many users still have an aging 802.11b/g router that barely does wired-equivalent-privacy (WEP) security. Even newer Wi-Fi equipment with Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2) may not be enough as you or someone else in your house most likely handout the access password to any guest you allow in the residence. Any malware on their systems now has the potential to infect other systems on your network and you have also given the keys to your local security to someone you may not fully trust. Many of the newest Wi-Fi access points – such as Apple AirPort Extremes and Netgear N[3|6]00s – provide for the ability to setup both a protected internal network and as open of a guest network as you want. I still suggest ensuring that the guest network be secured as you may be liable for any actions taken from your network (protected or otherwise).
Highway Safety
Being safe[r] on the Internet is much lke being safe[r] when driving a car. You need to make sure the fluids are at the right levels, that the tire pressure is sufficient for the driving conditions and that you wear your seatbelt before leaving the driveway. If you don’t regularly perform those tasks you run the risk of significant problems out on the road. You need to get in the habit of doing similar checks when navigating in potentially dangerous network territory as well. It doesn’t help that Facebook cares not a whit about your privacy or security and will seemingly randomly change your settings if it benefits them (or if they are just their usual incompetent selves). Want proof? You have to be diligent in the maintenance of all Internet security settings to ensure your consistent, personal online safety.
Those were the words that greeted me within five minutes of checking out the Flask microframework for Python web applications. I feel compelled to inline those four, short paragraphs:
I’m not joking. Well, maybe a little. If you write a web application, you are probably allowing users to register and leave their data on your server. The users are entrusting you with data. And even if you are the only user that might leave data in your application, you still want that data to be stored securely.
Unfortunately, there are many ways the security of a web application can be compromised. Flask protects you against one of the most common security problems of modern web applications: cross-site scripting (XSS). Unless you deliberately mark insecure HTML as secure, Flask and the underlying Jinja2 template engine have you covered. But there are many more ways to cause security problems.
The documentation will warn you about aspects of web development that require attention to security. Some of these security concerns are far more complex than one might think, and we all sometimes underestimate the likelihood that a vulnerability will be exploited, until a clever attacker figures out a way to exploit our applications. And don’t think that your application is not important enough to attract an attacker. Depending on the kind of attack, chances are that automated bots are probing for ways to fill your database with spam, links to malicious software, and the like.
So always keep security in mind when doing web development.
Let’s look at the key take-away messages…
Data Should Be Stored Securely
Interestingly enough, this is not the default mindset of one of the more popular modern database technologies [mongoDB] (and it has plenty of company [memcached], too).
Even if your app starts out without any real sensitive data, odds are you will be storing credentials, e-mail addresses, social network handles and other bits of information that you should feel some fundamental responsibility to treat with care. There are somemcached manymysql resourcesoracle tocouchdb helpsqlite that you really have no excuse.
And, it will save you time later on when you realize you actually need to have a secure storage foundation.
Watch The Input To Your Apps
Flask protects you against one of the most common security problems of modern web applications: cross-site scripting (XSS). There are many others. If you are a programmer and have never even heard of OWASP, then you need to put down your PS3/Xbox controller and do a quick read on at least their take on the top ten web app security risks (btw: there are way more than ten, but you need to start somewhere).
The thing is, unless the halls of higher education have crumbled completely since I was in school, I distinctly remember having the concept of input validation, bounds checking, etc. being rammed into my thick skull in almost every programming class (and this was way before web apps were even contemplated). You may think you’re innovating by posting a link to your functioning rapid prototype on Hacker News, but what you’re really doing is being sloppy, lazy and irresponsible. Period.
And, while it’s fine to seek out frameworks like Flask and rely on some of their inherent protections, it does not absolve you from your responsibility to deliberately & consciously build rugged software (which doesn’t just mean “secure”).
“Don’t think that your application is not important enough to attract an attacker”
I’m not sure if any amount of verbiage will convince someone of this fact if they are determined not to believe/accept it. It’s a much larger discussion (and this is already a long post). If you are inclined to have a slightly open mind, I encourage you to read So You Think Your Website Won’t Get Hacked by Joseph Schembr. It’s really slanted towards “script-kiddies,” but should pique your interest enough to keep exploring why your hacked-up personal URL shortener might be a target.
Fin
It’s impressive that the Flask authors cover security in some way, shape or form on 21 pages in the documentation [PDF]. If you’re building or contributing to other frameworks, projects or engines (hint, hint, Node.JS devs!) I would strongly encourage you to take as much time and consideration as the Flask team did to ensure you are making it as easy as possible for your users to deploy applications as securely as possible by default.